By Jacob Kushner, Anthony Langat, Sasha Chavkin and Michael Hudson
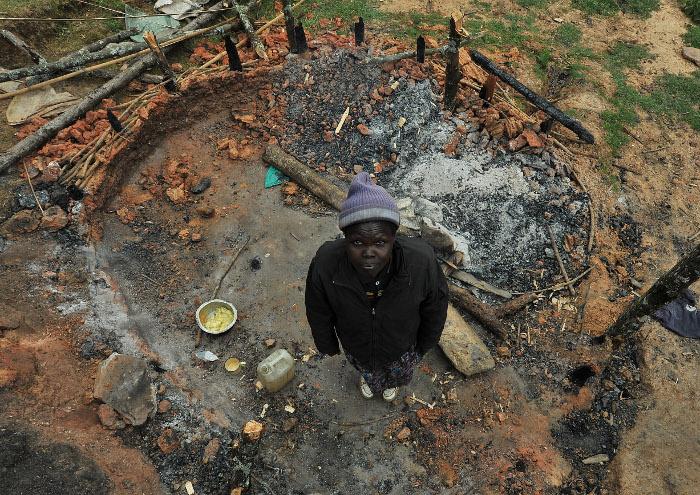
Gladys Chepkemoi was weeding potatoes in her garden the day the men came to burn down her house.
After her mother-in-law told her that rangers from the Kenya Forest Service were on their way, Chepkemoi strapped her 1-year-old son on her back and hurried to her thatched-roofed home. She grabbed two tins of corn, blankets, plates and cooking pans, and hid in a thicket.
She watched, she said, as the green-uniformed rangers set her house ablaze.
After they were gone, she came out of the thicket to see what was left.
“What used to be my home was now ashes,” she said.
The young mother is one of thousands of Kenyans who have been forced out of their homes since the launch of a World Bank-financed forest conservation program in western Kenya’s Cherangani Hills. Human rights advocates claim government authorities have used the project as a vehicle for pushing indigenous peoples out of their ancestral forests.
They are not alone.
In developing countries around the globe, forest dwellers, poor villagers and other vulnerable populations claim the World Bank — the planet’s oldest and most powerful development lender — has left a trail of misery.
Read the full story of the World Bank’s role in the displacement of the Sengwer at the Huffington Post or at GroundTruth. Jacob Kushner and Anthony Langat reported this story for GroundTruth. It is part of a larger project by the ICIJ that found the World Bank has displaced an estimated 3.5 million people across the globe in the name of “development.”
UPDATE: This investigation won the 2015 Online News Association Award for Investigative Journalism.
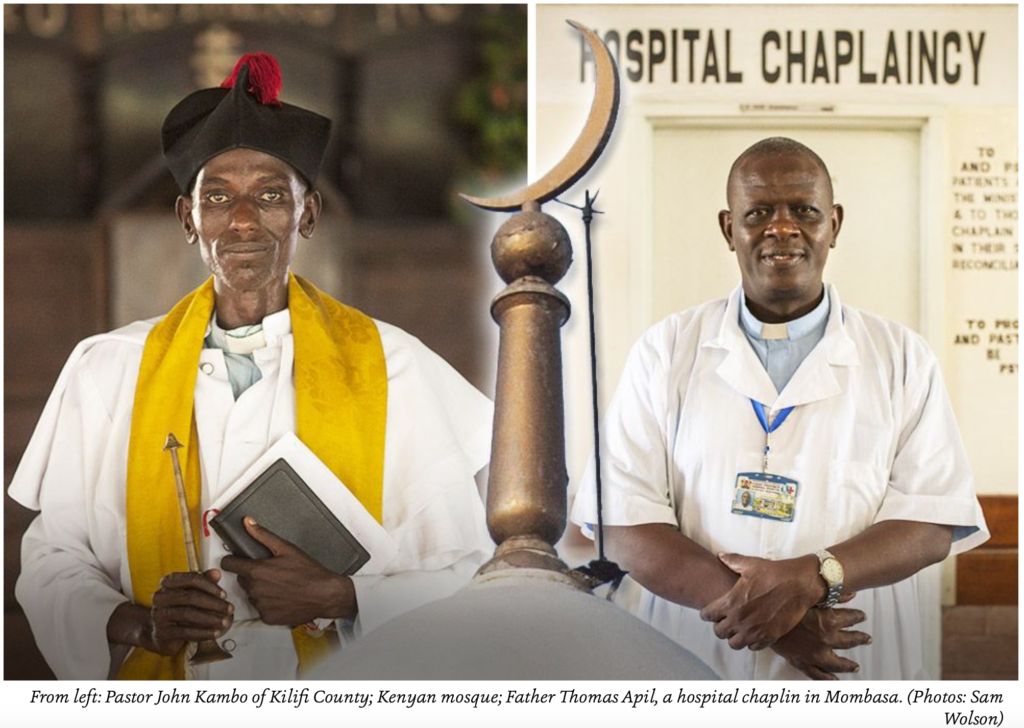 In an attempt to counter the anti-LGBT fervor gaining hold on Kenya’s coast, one gay rights organization has developed a new approach. Rather than confronting the religious leaders behind it, it’s inviting them to tea.
In an attempt to counter the anti-LGBT fervor gaining hold on Kenya’s coast, one gay rights organization has developed a new approach. Rather than confronting the religious leaders behind it, it’s inviting them to tea.
 NAIROBI, Kenya — Kenyan police have fueled the fires of Islamic extremism and may actually be undermining the country’s security in an overzealous attempt to protect it, according to human rights activists and advocates for police reform.
NAIROBI, Kenya — Kenyan police have fueled the fires of Islamic extremism and may actually be undermining the country’s security in an overzealous attempt to protect it, according to human rights activists and advocates for police reform.











