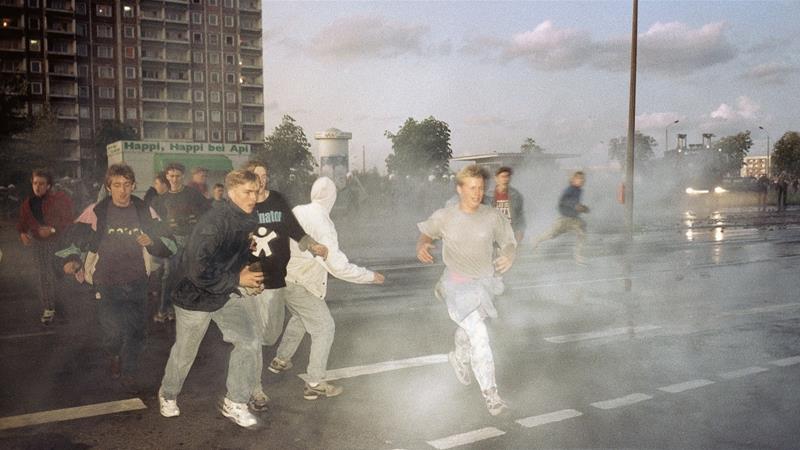

Right-wing extremists run through spray from water cannons during clashes between police and demonstrators in Rostock, Germany, on Monday, August 24, 1992 [Thomas Haentzschel/AP]
This summer marks the 25th anniversary of the Rostock riots – the most disturbing resurgence of anti-immigrant violence in Germany since the rise of Nazism.
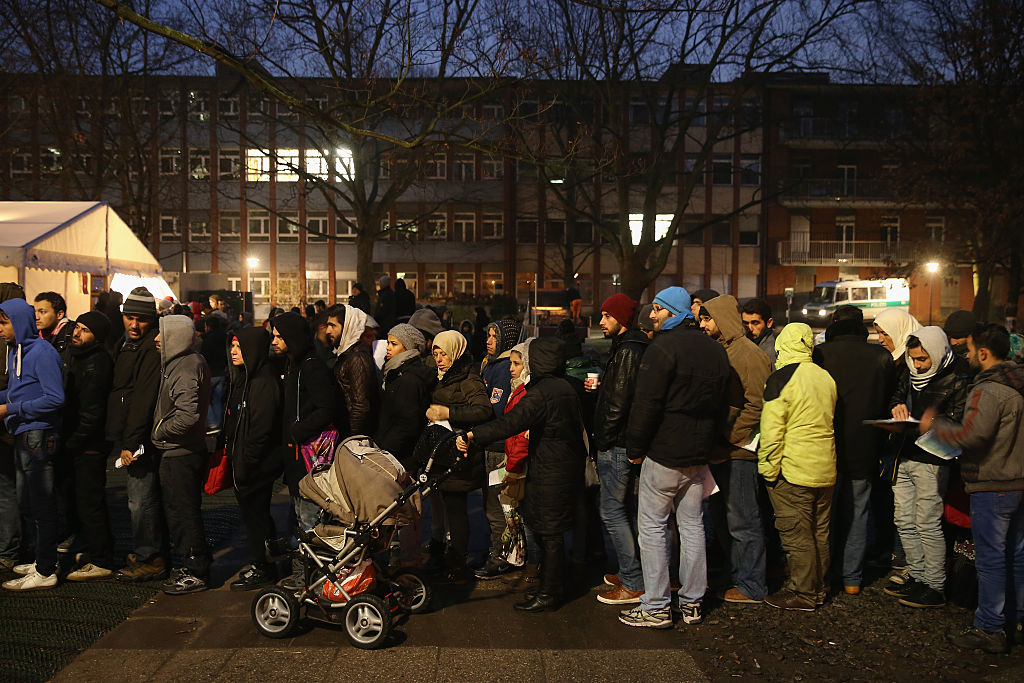
In the quarter of a century since, many foreigners arriving in Germany have experienced the warmest of welcomes – but a few have experienced chilling acts of hatred. This series explores how a small minority of ultra-xenophobic Germans has tarnished their nation’s reputation as a haven for the world’s displaced masses. These stories are primarily told through the experiences of immigrants and asylum seekers who survived xenophobic harassment or attacks.
 Their stories are the exception to the norm: incidents of violent xenophobia are rare in Germany compared with other countries. Indeed, Germany has welcomed more asylum seekers in recent years than any other European nation – the United Kingdom, France, Poland, Austria, Hungary, and magnitudes more than the far more populous United States. When faced with the largest exodus of people since World War II, none of these nations welcomed refugees as unconditionally as Germany did. It’s precisely because of this reputation that Al Jazeera is taking a hard look at what happens on the occasions when that welcome culture goes awry.
Their stories are the exception to the norm: incidents of violent xenophobia are rare in Germany compared with other countries. Indeed, Germany has welcomed more asylum seekers in recent years than any other European nation – the United Kingdom, France, Poland, Austria, Hungary, and magnitudes more than the far more populous United States. When faced with the largest exodus of people since World War II, none of these nations welcomed refugees as unconditionally as Germany did. It’s precisely because of this reputation that Al Jazeera is taking a hard look at what happens on the occasions when that welcome culture goes awry.
This is the first story in a 7-part series. Read it at Al Jazeera.
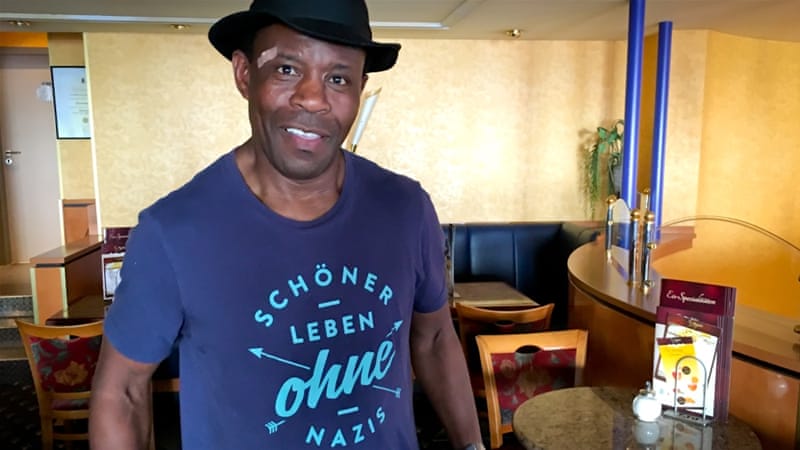
Story 2: Ibraimo Alberto, a Mozambican immigrant and child of former slaves, encountered many opportunities in Germany. But he also experienced racism, big and small, in the east and west– including the murder of a friend. Read his story at Al Jazeera.
Story 3: The climate of fear and tension among more recent refugees arriving to Germany reached a climax one afternoon in October 2015 when a 32-year-old German man enticed a four-year-old Bosnian boy named Mohamed away from his family and abducted him. Read the story at Al Jazeera.
Story 4: On a cold night last year, some 70 Germans, mostly men, surrounded a bus of refugees in the small town of Clausnitz and chanted at them to “go home”. On the bus were 15 asylum seekers from Syria, Lebanon, Iran and Afghanistan. Their hostile reception by protesters who blocked their path made international headlines, reinforcing stereotypes of small-town Germans as racist and blemishing Germany’s so-called “welcome culture.” Neither the refugees nor the demonstrators wanted this. But then, neither had a choice. Read the story at Al Jazeera.
Story 5: On Halloween night, Abu Hamid went into the kitchen to grab some food when he noticed sparks of light outside the window. Sensing danger, he and his roommates rushed out of the kitchen just as a booming explosion shook the house, shattering the windows and sending pieces of glass into one man’s face. Local police had failed to see a connection between a series of right-wing protests against refugee housing shelters. It wasn’t until news outlets as far away as Berlin began pressuring authorities to take action that Germany’s federal prosecutor took up the case. In a dramatic SWAT-style raid, federal and state police arrested five suspects believed to have formed an organised anti-refugee militia. Read the story, Escaping Aleppo only to encounter terrorism in Germany, at Al Jazeera.
Story 6: A lawyer and his family fled death threats in Pakistan, so they flee to Germany for safety. Instead, their building is attacked–firebombed–by right-wing Germans. Khan wondered whether Germany would accept their asylum applications, and allow them to stay. “Tomorrow, I don’t know what will happen,” Khan said. “Maybe Germany will say, ‘Out!'” In fact, it did. Read the full story at Al Jazeera.
Story 7: Each week in Dresden, a group of refugees and Germans gather at a nondescript cafe hidden from view, pushed back from the street. The cafe provides a safe space for them to mingle with the locals to chat, practise their language skills, and sip tea and juice. It’s one of many spaces that have popped up across Germany to welcome refugees, help them with their asylum applications, teach them German, or just for engagement.
But this particular space, known as the “international cafe”, rests in an uncanny location. Dresden, the capital of Saxony, is a stronghold for Germany’s anti-immigrant politics. Each week, thousands of protestors chant that refugees should “go home” and denounce what they see as the Islamisation of Germany. Read the full story at Al Jazeera.












 Last year at primary schools in western Kenya, social scientists were busy performing dirty skits in front of hundreds of children. The script went like this:
Last year at primary schools in western Kenya, social scientists were busy performing dirty skits in front of hundreds of children. The script went like this:

 Young people across the continent aspire to careers in Africa’s blossoming information and communications technology (ICT) sector. But many encounter major barriers that prevent them from finding jobs in the industry. “We have a lot of young people. But unfortunately they come from neighborhoods that don’t have a lot of opportunities,” says Tim Nderi, the chief executive officer of Mawingu Networks.
Young people across the continent aspire to careers in Africa’s blossoming information and communications technology (ICT) sector. But many encounter major barriers that prevent them from finding jobs in the industry. “We have a lot of young people. But unfortunately they come from neighborhoods that don’t have a lot of opportunities,” says Tim Nderi, the chief executive officer of Mawingu Networks.